NLR Blog
Thursday, January 31, 2008FCC Rural Health Care Pilot Project Service Provider Conference Call
The USAC folks have scheduled a service provider conference call for Thursday, February 7 at 2 pm Eastern time. Details will be posted here when available.
This call is for service providers who might want to bid on the Rural Health Care projects. Services such as network design, network management, and circuit provisioning will be discussed.
A Blueprint for Big Broadband
This report proposes bringing the federal government, state governments, and the private sector together as part of a new approach to making high-speed Internet services available across the country. The report also contains a detailed analysis of broadband deployment in the United States and in key countries around the world.
http://connect.educause.edu/Library/Abstract/ABlueprintforBigBroadband/45996?time=1201816531
Calit2 and University of Melbourne Initiate Australia's Ultra-Resolution Global Collaboration Laboratory
Bringing the OptIPortal and gigabit/s super-broadband networking together is the cutting-edge expertise of two of the world’s leading telecommunications research units: the University of Melbourne School of Engineering’s Centre for Ultra Broadband Information Networks (CUBIN), and the California Institute for Telecommunications and Information Technology (Calit2), a UCSD/UC Irvine partnership.
The link-up was made possible by use of the high-capacity backbone of AARNet, Australia’s academic and research network, with a connection to the U.S. West Coast using SXTransPORT on the Southern Cross Cable Network to the Calit2 network in San Diego via Pacific Wave and CENIC.
Calit2 Director Larry Smarr notes that today’s demonstration marks the entry of Australia into the growing OptIPlanet Collaboratory, enabling innovators around the world to work together on major data-intensive scientific, medical, and environmental challlenges: “Based on today’s success, we will connect other Australian universities with universities in the United States and around the world using these advanced technologies in 2008.”
For the full article, visit http://www.calit2.net/newsroom/release.php?id=1219NIST Publishes a Draft IPv6 Profile in the U.S. Government
GRNOC Real-time Atlas
SANRAD Delivers Disaster Recovery
The Northwest Regional Data Center (NWRDC),Florida's leading
computing data center for educational and governmental communities,
has deployed six SANRAD V-Switches to manage growing volumes of
archived data and protect against loss.
NWRDC provides data security, accessibility and connectivity
services to more than 80 Florida-based customers, including K-20
educational facilities, major research universities and local
governments. With a growing customer base and increasing amounts of
data to protect, NWRDC was facing a mounting disaster recovery risk
and dealing with a manual off-site storage process for archive tapes
that was cumbersome and difficult to manage. The NWRDC solution
connects the organization's mainframe system to a pair of SANRAD
V-Switches, which transfer data via the Florida Lambda Rail and
Southern Light Rail dark fiber networks to a Category 5 hot site in
Atlanta. There, NWRDC's data is securely housed and easily recovered
in the event of downtime or disaster.
See the entire release at http://tinyurl.com/2q2agr.
NLR Update at Joint Techs
Highlights include:
Lighting of the Boston node
Cisco Telepresence support hardware available for use
Availability of dynamic VLAN provisioning
Peering with the National University of Singapore
Science and Engineering Indicators 2008
The National Science Board’s Science and Engineering Indicators 2008 is now available online. The report presents information on science, mathematics, and engineering education at all levels; the scientific and engineering workforce;
Visit http://www.nsf.gov/statistics/seind08/ for more information.
MIT Launches Regional Optical Network
It's huge and it's fast and it's just been unleashed. The new MIT Regional Optical Network provides connectivity to key Internet exchange points with speeds beyond 10 Gbps, the equivalent of transmitting 10 full-length, high-definition movies in 30 seconds. This all-optical intelligent network is one of the world's largest institutional networks for research and collaboration.
IS&T partnered with Nortel to create this next-generation network, acquiring already-laid fiber-optic lines (“dark fiber”) from Level 3 Communications and Vermont Telephone. The network is designed to accommodate faster technologies and upgrades as they become available. Initially, it is being deployed across the northeast United States, connecting MIT's main campus to New York, Washington, D.C., and Baltimore via 1500 miles of fiber, with optical equipment at seventeen locations across seven states. Plans include linking to LHCnet, the research network maintained by the European Organization for Nuclear Research (CERN); the Energy Sciences Network (ESnet); and the National LambdaRail. All are comprised of millions of network elements.
Tech Specs
IS&T's ultimate objective is to help create the fastest and most flexible network possible, one with the potential to revolutionize education, collaboration, and the sharing of research. The solution is built on Nortel's Common Photonic Layer (CPL). CPL provides for rapid provisioning of changing service and traffic patterns across the network. The CPL, combined with the Nortel Optical Multiservice Edge 6500, enables the flexibility to add a multitude of network services across the 10G infrastructure as required.
From http://web.mit.edu/ist/news/spotlight/
Conrad named vice chancellor for information technology, chief information officer
The UNC Board of Trustees approved Conrad’s appointment, effective Feb. 1, 2008. Conrad will succeed Dan Reed, who became director of scalable computing at Microsoft Research earlier this month.
Conrad led the effort to define and build a new high-speed research and education network in Florida known as the Florida LambdaRail, which provides opportunities for Florida university faculty, researchers and students to collaborate with colleagues worldwide.
In addition, he previously served on the board of the National LambdaRail, a nationwide high-speed research network initiative.
For the full press release, visit http://tinyurl.com/yploln
FCC Rural Health Care Pilot Program Website is Up
You can find everything you need for the RHCPP at their new website. USAC (Universal Service Administrative Company) will provide the selected participants with guidance on the process to receive funding, how to fill out the proper forms, and other program related information.
Check it out at http://www.usac.org/rhc-pilot-program/TeraGrid-II: a vision toward the 21st century integrated knowledge infrastructure
"Knowledge in the twenty-first century is profoundly determined by the convergence of multiple disciplines and approaches for problem solving. Collaboration is required to help not only improve but understand intersections in scientific endeavor while creating a common language that permits close interaction among researchers, administrative personnel, and society in general. Creation of new knowledge –the expected outcome at the end of the line in Science– is a process that requires infrastructure to support information exchange, analysis, and representation as well as collaborations. The Grid in the latter sense has become an essential fabric for that Cyberinfrastructure: it attempts to provide coordination of computing infrastructure in a seamless way with increasing efficacy while considering security, privacy and efficiency following the metaphor of the electric power grid where users connect as long as the meet the technical specifications3."
To read more visit http://tinyurl.com/3cvbqg
FCC Rural Health Pilot Program Update
On Tuesday, September 26, 2006, the Federal Communications Commission announced the establishment of a pilot program to help public and non-profit health care providers build state and region-wide broadband networks dedicated to the provision of health care services, and connect those networks to Internet2 or National LambdaRail. The pilot program will fund up to 85% of the costs incurred to deploy state or regional broadband networks dedicated to health care and up to 85% of the costs of connecting the regional and/or statewide to Internet2 or National LambdaRail.
All service providers (including RONs) that wish to participate in the Rural Health Care Program must have a Service Provider Identification Number (SPIN) issued by USAC.
The Service Provider Identification Number (SPIN) is a unique number assigned to each service provider by USAC. The SPIN serves as USAC's tool to ensure that support is directed to the correct service provider. Once USAC establishes the SPIN, the service provider's name, contact information, and SPIN are forwarded to USAC to confirm eligibility.For more information about obtaining a SPIN, call USAC's Client Services Bureau at 1-888-641-8722 or visit the USAC website at http://www.usac.org/rhc/about/rhc-pilot-program.aspx
Downloadable Map and Regional Contacts List
The map is formatted to conveniently be printed on one 8.5x11 inch sheet of paper.
NLR connectivity is easy. NLR provides a variety of national backbone options. An NLR member or associate organization coordinates the regional networking components. An individual institution coordinates a local campus connection.
Joint Techs Workshops in January
Joint Techs Workshops are an international conference of networking engineers featuring presentations, Birds-of-a-Feather meetings and demonstrations of state-of-the-art high-performance networking technologies. The Winter 2008 Joint Techs will focus on Hybrid Networking, The Coming Crisis in Routing and Addressing, and Security.
http://tinyurl.com/2r597h
NLR Weathermaps
http://noc.nlr.net/nlr/network-status.html
Click on the Weathermap under the different NLR services -- Wavenet, Framenet and Packetnet to see traffic levels.
'Shot in the Dark' Star Explosion Stuns Astronomers
http://hpwren.ucsd.edu/news/20071221/
'Shot in the Dark' Star Explosion Stuns Astronomers
By W. Scott Kardel, Public Affairs Coordinator, Palomar Observatory
Last January, NASA's Swift satellite detected another gamma-ray burst and quickly sent its alert to ground-based astronomers. Palomar Observatory's 60-inch telescope was one of the first to respond. The 60-inch, and indeed the entire observatory, is linked into the High Performance Wireless Research and Education Network (HPWREN). HPWREN enabled the message from Swift to be received, allowing the automated 60-inch telescope to quickly measure the fast-fading visible-light afterglow of the GRB. Data was then sent away from Palomar. Measurements prompted observations with the giant 8-meter Gemini North telescope and the 10-meter Keck I telescope. From this astronomers were able to determine the distance to the GRB - 9.4 billion light-years distant. The burst are short lived. Without the rapid transfer of data in and out from Palomar the response to the burst wouldn't be possible.
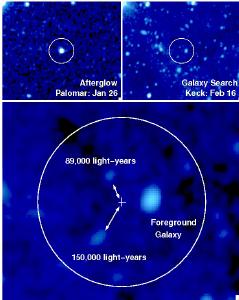 |
Measurements indicated that this burst was likely produced by the collapse and explosion of a massive star. These stars "live fast and die young" and are expected to be found in a galaxy where new stars are being produced, yet deep images from Keck failed to find any signs of a galaxy. This means there shouldn't have been that type of star there.
So where did this burst come from? Maybe a faint tidal tail, produced as galaxies collide, is lurking too faint for even Keck to see. Maybe our understanding of this type of GRB is flawed. Deep searches with the Hubble Space Telescope hope to answer the question soon. Stay tuned.
The full story is at: http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/news/topstory/2007/intergalatic_shot.html.
